This may interest people – it comes from a paper that systematically reviewed the literature on the antecedents of safety cognition in construction workers.
Cognition is “all processes by which … sensory inputs is transformed, reduced, elaborated, stored, recovered, and used”.
It’s great that they broadened cognition from just an individual process to the broader system (more akin to distributed cognition, even though they didn’t talk about this directly).
It is conceptualised to have different stages, being:
· Obtaining information (sensing and perception)
· Understanding information (hazard identified and risk perception)
· Response selection
· Execution
The attached figure highlights the relationships among the identified antecedents of cognition identified in the study.
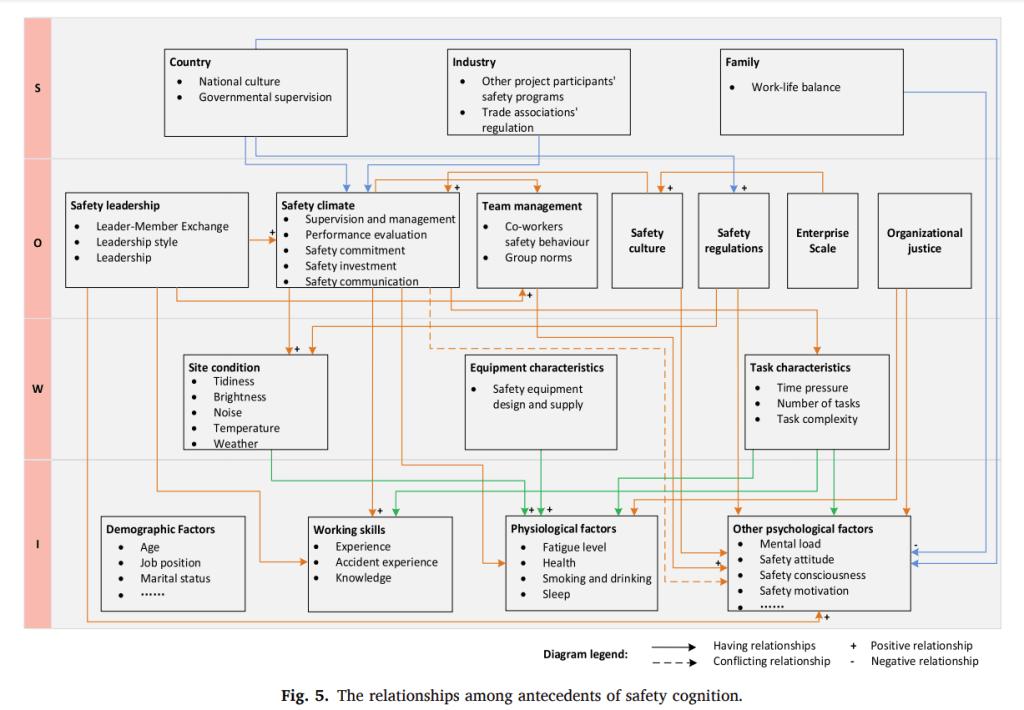
Antecedents of cognition are distributed across several layers, see the left column in the figure. S = social factors, O = organisational factors, W = work situational factors, I = individual factors.
Relationships between social factors and other levels are represented by the blue lines. Social factors are said to be closely related to organisational factors.
They observe that “In terms of national culture, it has been found that there are significant differences between domestic workers and foreign workers in the perception of safety climate, and the perception of safety climate is poor among foreign workers”.
Differences among groups with differing sub-cultures also have been shown to have differing attitudes and perception of risk.
Industry factors relevant to cognition include safety programs that affect safety climate, and other org designs/interventions that improve work-life balance.
Next are relationships between organisational factors and other levels (orange lines). Safety training has captured a lot of research here. Safety training has shown links with enhancing knowledge (as predicted), and also influencing perceived work control and driving safety consciousness.
Other factors like safety commitment can predict fatigue and mental load, and organisational communication is positively correlated with team communication. Leadership has also captured a lot of research, with positive links between safety leadership and worker psychological safety, motivation, safety climate and more.
Finally there are links between work situational factors and other levels (green lines). These are said to be closely related to fatigue and mental load of workers, and includes things like poor site conditions, poor safety equipment, design, time pressure, massive tasks, high task complexity.

Authors: Liu, Y., Ye, G., Xiang, Q., Yang, J., Goh, Y. M., & Gan, L. (2023). Antecedents of construction workers’ safety cognition: A systematic review. Safety science, 157, 105923
Study link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2022.105923
One thought on “Systematic review of the antecedents involved in construction worker cognition and risk perception”