Not much to say, just an extract from Andrew Hopkins’ 2006 paper ‘Studying organisational cultures and their effects on safety’.
I’ll be posting the summary in the coming weeks.
Here he describes his analysis of the 1999 Glenbrook rail crash:
· He identified four main cultural themes preceding the disaster
· First “the railways were obsessively rule focused, in ways that hindered safety”
· Second “the railway system was organisationally and occupationally fragmented, resulting in a culture of silos”
· Third “there was a powerful culture of punctuality – on-time-running”
· Fourth “the culture was risk-blind, even risk-denying”
· The risk blindness was similar to works by Turner and Vaughan
· Turner’s work, “was largely about how it is that organisations develop cultures of risk denial”
· Vaughan described NASA’s cultures as a “way of seeing that is simultaneously a way of not seeing”
· Hopkins proposed that the four cultural elements in the diagram “gave rise to the accident” (image 1)
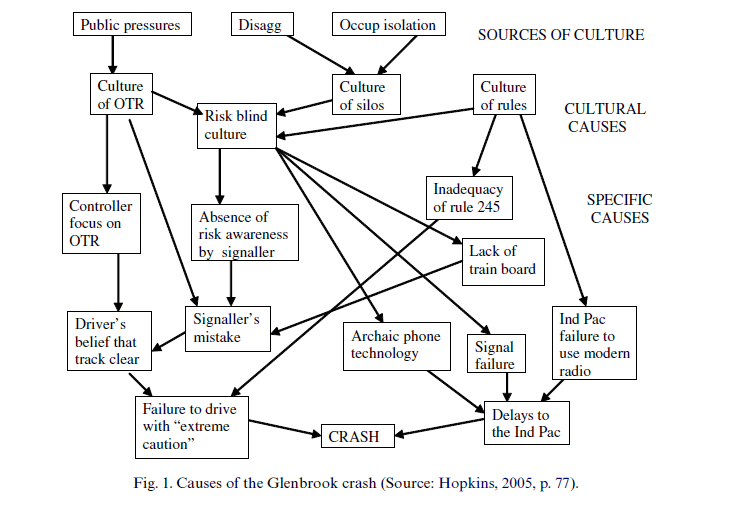
· He asks that since these cultural elements are “research constructs, not explicitly identified by witnesses, how is their validity to be established?”
· He proposes ways of establishing validity to the ideas. Based on Schein, one means is whether people from within that culture see the findings as credible
· Hence if “these descriptions are recognisable or at least plausible based on other organisations of which outsiders have some knowledge”, then they can be considered credible
· In any case, according to Geertz, “ethnographic descriptions are “essentially contestable”
· Also, “It should be noted that identifying cultural elements that have contributed to an accident involves no automatic judgments about their desirability”
· There is also “no presumption that these values are necessarily a bad thing”
· E.g. a culture of on-time-running is “clearly desirable for rail
organisations; it is only when it takes priority over safety that it becomes problematic”
For reference, image 2 is an example of Hopkins’ analysis of the Australian Air Force health exposure event.

Ref: Hopkins, A. (2006). Studying organisational cultures and their effects on safety. Safety science, 44(10), 875-889.

Study link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2006.05.005