
Can LLM’s effectively play as devil’s advocate, enhancing group decisions?
Something I’ve been working on lately is AI as a co-agent for cognitive diversity / requisite imagination.
Here’s a study which explored an LLM as a devil’s advocate, and I’ll post another study next week on AI and red teaming.
[Though this study relied on a single LLM, another study used a multi-model approach.]
For methods, they had human groups assess recidivism risk with the assistance from intentionally biased AI models. An LLM devil’s advocate was also introduced with varying target of objection
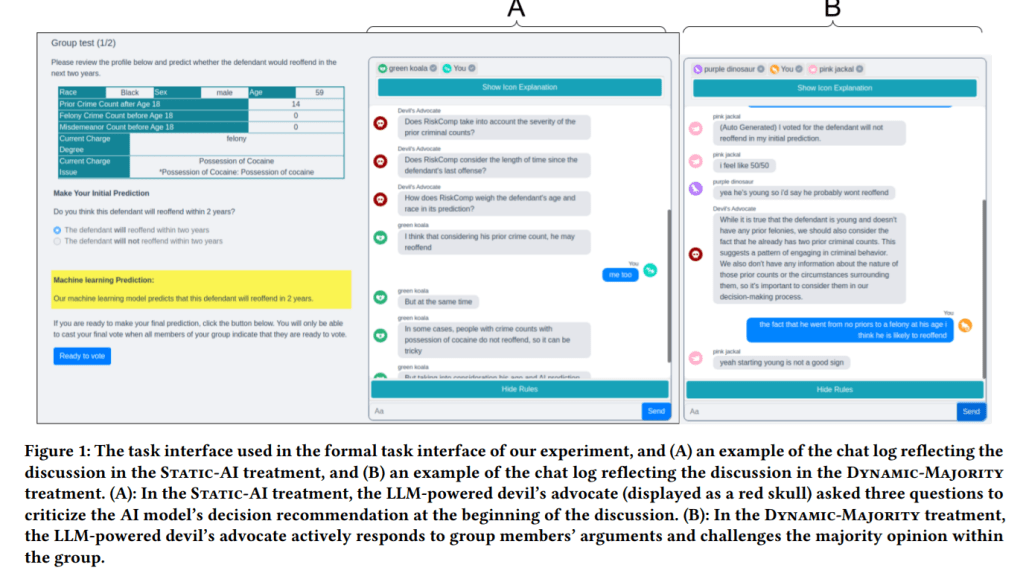
Findings:
· Groups with the LLM devil’s advocate that challenged the AI model’s recommendation showed a “significantly higher level of accuracy in solving the decision making tasks”
· The “increase in groups’ decision accuracy… mainly occurs on in-distribution task instances”
· “The inclusion of the devil’s advocate in the AI-assisted group decision making process generally makes group members engage in longer discussions… especially for groups in the Dynamic-AI treatment”. This indicates the devil’s advocate “increases the “amount” of deliberation”
· The devil’s advocate in the Dynamic-AI treatment also “appears to encourage participants to make predictions in a more systematic manner by having them examine a more comprehensive set of factors and constantly reflect on the soundness of their decision arguments,” thus helping “increase the “quality” of deliberation as well”
· “The devil’s advocate designed to challenge the majority opinion within the group does not appear to significantly influence how appropriately groups utilize AI assistance”
· When an interactive devil’s advocate challenged the majority opinion, it “results in shorter discussions compared to when it challenges the AI model”
· LLMs “are mainly designed and fine-tuned for one-on-one conversations,” and their traditional design “has limitations that potentially hinder their effectiveness” in multi-person group discussions
However, they note that prior research on AI/LLM group interactions:
“groups exhibit a higher level of over-reliance on AI [14], potentially as some group members experience an “anchoring effect” [28] by treating AI recommendations as reference points while others have the desire to “follow the crowd” [68] or to avoid social collision”
Ref: Chiang, C. W., Lu, Z., Li, Z., & Yin, M. (2024, March). Enhancing ai-assisted group decision making through llm-powered devil’s advocate. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (pp. 103-119).

Shout me a coffee (one-off or monthly recurring)
Study link: https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3640543.3645199
Safe As LinkedIn group: https://www.linkedin.com/groups/14717868/
